Introduction:
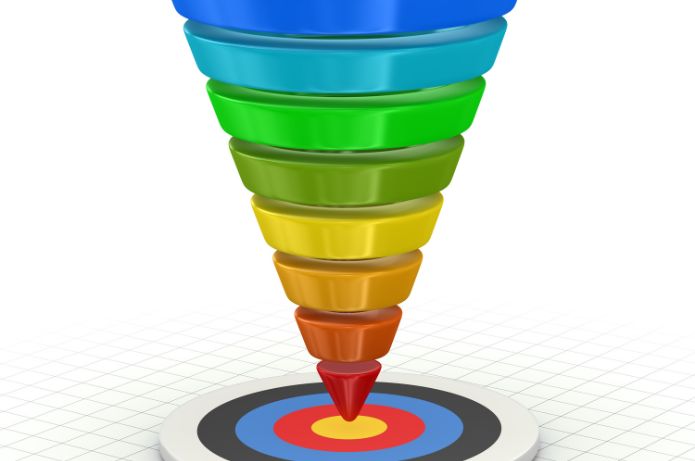
The Sales Funnel, also known as the Conversion Funnel or Sales Pipeline, is a fundamental concept in marketing and sales. It visually represents the process that potential customers go through, from the first contact with a company or product to the purchase. This model helps organizations understand and optimize the customer journey, identifying points of improvement and conversion opportunities at each stage of the process.
1. Definition and Concept:
The Sales Funnel is a metaphorical representation of the path that a potential customer takes from the moment they become aware of a product or service until the purchase is completed. The funnel shape is used because, typically, the number of people decreases as they progress through the stages of the purchasing process.
2. Basic Structure of the Sales Funnel:
2.1. Top of the Funnel (ToFu – Top of the Funnel):
– Awareness: At this stage, the goal is to attract the attention of as many potential customers as possible.
– Strategies: Content marketing, advertising, social media, SEO.
2.2. Middle of the Funnel (MoFu – Middle of the Funnel):
– Consideration: Leads begin to evaluate the options available in the market.
– Strategies: Email marketing, webinars, case studies, product demonstrations.
2.3. Bottom of the Funnel (BoFu – Bottom of the Funnel):
– Decision: The potential customer is ready to make a choice.
– Strategies: Personalized offers, free trials, individual consultations.
3. Importance of the Sales Funnel:
3.1. Process Mapping: Helps visualize and understand each stage of the customer journey.
3.2. Bottleneck Identification: Allows identifying where leads are dropping out of the process.
3.3. Resource Optimization: Facilitates the efficient allocation of marketing and sales resources.
3.4. Sales Forecast: Assists in predicting future revenue based on lead flow.
4. Important Metrics:
4.1. Conversion Rate: Percentage of leads that move from one stage to another.
4.2. Sales Cycle Time: Average duration of the process from the first contact to the sale.
4.3. Cost per Lead: Investment needed to attract each potential customer.
4.4. Average Sale Value: Average revenue generated per converted customer.
5. Evolution of the Concept:
5.1. Traditional Sales Funnel vs. Modern Sales Funnel
– Traditional: Linear and unidirectional.
– Modern: Non-linear, considering multiple points of contact and interactions.
5.2. Omnichannel Sales Funnel
Integrates different communication and sales channels, offering a cohesive customer experience.
6. Strategies for Funnel Optimization:
6.1. Audience Segmentation: Customize the approach for different customer profiles.
6.2. Lead Nurturing: Nurturing relationships with relevant content over time.
6.3. Marketing Automation: Use tools to automate interactions and follow-up.
6.4. Data Analysis: Using data-driven insights to refine strategies.
7. Common Challenges:
7.1. Alignment between Marketing and Sales: Ensuring that both teams work in harmony.
7.2. Lead Qualification: Correctly identify the leads most likely to convert.
7.3. Personalization at Scale: Offering personalized experiences to a large number of leads.
7.4. Adapting to Changes in Consumer Behavior: Keep the funnel updated according to market trends.
8. Sales Funnel in the Digital Context:
8.1. Inbound Marketing: Attract clients through relevant and non-intrusive content.
8.2. Retargeting: Reconnect with leads who previously showed interest.
8.3. Social Selling: Using social networks to build relationships and generate sales.
9. Tools and Technologies:
9.1. CRM (Customer Relationship Management): Systems to manage interactions with customers.
9.2. Marketing Automation Platforms: Tools to automate campaigns and nurturing.
9.3. Analytics: Solutions for data analysis and insight generation.
10. Future Trends:
10.1. AI and Machine Learning: Use of artificial intelligence to predict behaviors and personalize interactions.
10.2. Augmented and Virtual Reality: Immersive experiences for customer engagement.
10.3. Hyper-personalization: Offering highly customized experiences based on detailed customer data.
Conclusion:
The Sales Funnel is an essential tool for companies seeking to understand and optimize their customer conversion process. By mapping the customer journey and identifying improvement opportunities at each stage, organizations can significantly increase their conversion rates and enhance the overall customer experience.
11. Practical Implementation of the Sales Funnel:
11.1. Mapping of the Current Process
– Identify all existing steps in the sales process.
– Analyze customer contact points at each stage.
11.2. Definition of Objectives
– Establish clear goals for each stage of the funnel.
– Determine relevant KPIs (Key Performance Indicators).
11.3. Creation of Specific Content
– Develop appropriate materials for each phase of the funnel.
– Align content with customer needs and questions at each stage.
11.4. Implementation of Monitoring Systems
– Use CRM tools to track the progress of leads.
– Set up alert systems for leads that need attention.
12. The Role of Consumer Psychology in the Sales Funnel:
12.1. Emotional Triggers
– Use elements that appeal to consumers’ emotions at different stages.
– Understand the motivations underlying purchasing decisions.
12.2. Principle of Scarcity
– Apply tactics that create a sense of urgency and exclusivity.
12.3. Social Proof
– Incorporate testimonials, reviews and success stories throughout the funnel.
13. Sales Funnel for Different Business Models:
13.1. E-commerce
– Focus on cart abandonment and re-engagement tactics.
– Using remarketing to win back visitors.
13.2. B2B (Business-to-Business)
– Longer and more complex sales cycles.
– Emphasis on building relationships and demonstrating long-term value.
13.3. SaaS (Software as a Service)
– Using free trials and demos as a crucial part of the funnel.
– Focus on efficient onboarding and customer retention.
14. Integrating the Sales Funnel with After-Sales:
14.1. Customer Success
– Ensure customer satisfaction after purchase.
– Identify upsell and cross-sell opportunities.
14.2. Loyalty Programs
– Implement strategies to keep customers engaged and loyal.
14.3. Feedback Loop
– Use post-sale insights to improve previous stages of the funnel.
15. Advanced Metrics and Data Analysis:
15.1. Lifetime Value (LTV)
– Calculate the total value that a customer generates throughout their relationship with the company.
15.2. Churn Rate
– Monitor customer churn rate and identify patterns.
15.3. Cohort Analysis
– Group customers based on common characteristics for more accurate analysis.
16. Ethical and Privacy Challenges:
16.1. Compliance with Regulations
– Adapt strategies to comply with laws such as GDPR, CCPA, LGPD.
16.2. Transparency:
– Be clear about how customer data is collected and used.
16.3. Opt-in and Opt-out
– Give customers control over their information and communication preferences.
Final Conclusion:
The Sales Funnel is much more than a simple visual representation of the sales process. It is a strategic tool that, when properly implemented and optimized, can significantly transform a company's results. By deeply understanding each stage of the funnel, organizations can create personalized and relevant experiences for their potential customers, increasing conversion chances and building lasting relationships.
As consumer behavior evolves and new technologies emerge, the Sales Funnel concept will continue to adapt. Companies that stay agile, customer-focused, and willing to innovate in their sales and marketing approaches will be better positioned to achieve success in the current competitive market.
Ultimately, the Sales Funnel is not just about converting leads into customers, but about creating a cohesive, informative, and satisfying customer journey that benefits both the company and the consumer. By implementing the strategies, tools, and insights discussed in this article, organizations can create an effective sales funnel that not only generates results but also builds a solid foundation for sustainable growth and long-term success.